

Injection molding is one of the famous and vital technologies for mass-producing items out of thermoplastic, usually without post-finishing. Modern injection molding machines mainly produce universal-type molding machines that are urban-type and can make all sorts of part cases within limitations. Regarding the initial economics process, this method best fits articles with complex geometry and can be applied preferentially to other methods. The cost per molding is positively proportional to scale, yet the vast initial investment in injection molding needs to be clarified.
The injection molding process begins with the addition of plastic pellets and metal powder to the hopper of the injection molding machine. The hopper then feeds the plastic into the barrel, heating it to a liquid state. Molten plastic and metal enter the mold through the barrel using the nozzle.
The extruder has a nozzle. It is pressed tightly into a recess in the stationary portion of the mold. The two halves, with the vertical parting surface, are made of heavy steel and secured to thick steel tie-bars. The system of runners contained within the injection mold is designed to disperse the melt from the sprue to the cavity, which determines the product dimensions. The mold halves are held together under high pressure from a hydraulic piston using dedicated clamp plates.
The channels of cooling that pass through the cavities make the mold cold, which is a low point below the melting point of the plastic or other material. After this, the screw moves forward, and pushes the melt through the runners into the cavities, by maintaining the melting pressure.
Finally, the injection mold machine's clamping force is released, and the ejector pins of the opposite half of the mold are activated, forcing the molded part and runners out of the mold halves. Meanwhile, the extruder moves backward, and more hot melt is produced.
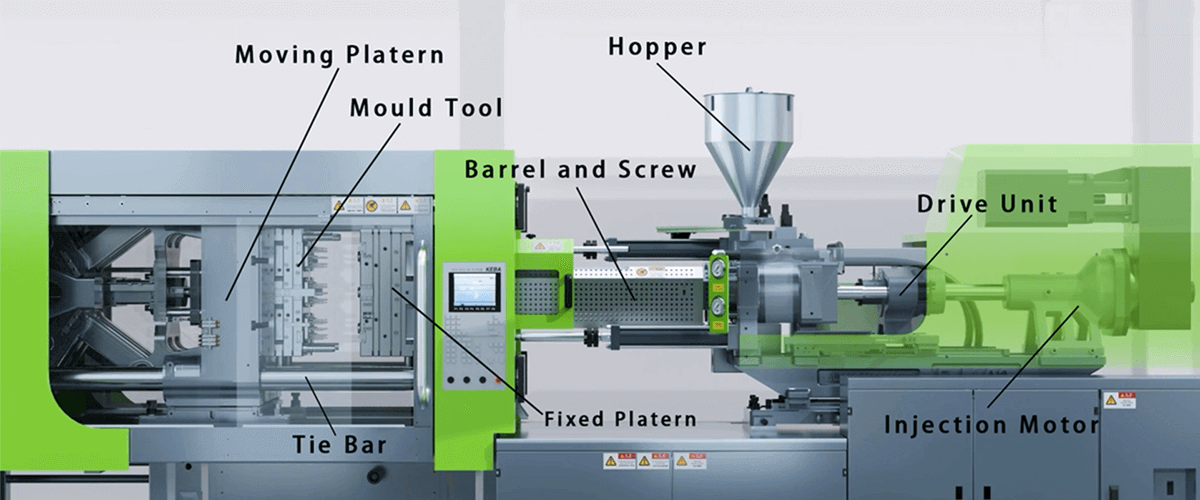
An injection molding machine is comprised of four main components: the lower one, the middle one, the barrel, and the clawing unit. It also has many other parts, including a nozzle, ejector pins, split mold, clamping unit, injection unit, and hydraulic unit.
The frame holds all the other parts and electronics required for the machine to function. The device's reasonably sophisticated electronics must deal with everything from a wide variety of hydraulic heaters to sensors and different injection pressures.
Below you’ll find the components of injection molding and how they work:
The hopper contains plastic pellets poured into the unit where the injection molding process can start. The dryer part is an essential element of a hopper - it ensures that the moisture level does not deteriorate while the material is inside the hopper. Additionally, it could have magnets as small as possible to protect the robot from any hazardous metallic particles that may enter the robot. After that, the mold is placed in the base of the injection molding equipment, and the plastic material is extruded into the hopper, which is consistent with the part shape called the barrel.
The barrel, which involves the mold and barrel, melts the polymer into a molten situation to fill the molten mass from the barrel. The screw that is delivering the plastic inserts it into the dumpers through the clamping unit. So, the barrel needs efficient temperature regulation to have a consistent temperature for each type of plastic material. The cylinder is the critical component that performs the task of carrying, compressing, melting, mixing, and pressing, forming the plastic into the machine.
Injection molding machines may use their heaters differently, which are meant to warm up conduits and nozzles, molds, and platens. The barrel where the material will be extruded can be fitted with a heating unit that will melt the hopper's molding material and make it into a liquefied state. For example, some injection molding heaters include band heaters, coil/nozzle heaters, cartridge & strip heating implications, and insulated cloth heating jackets.
The nozzle is an injection molding component situated at the bottom edge of the machine's ejector system. It propels the molten plastic from the cannon through the nozzle and into the dye set. A nozzle rests against a surface of the mold called a sprue bush and locating ring, which assists in retaining the nozzle in the center of the mold. The nozzles enable a diversity of operations, including filtering, mixing, and shutting off the melt flow.
Nozzle filters will decrease the residue damage on gates and hot runner tips from unwanted materials and contaminations. Mixed nozzles may promote better additive dispersion and mixing in molds, contributing to the overall part quality, low volume, and low additives cost. Shut-off nozzles substantially reduce melt froth in injection molding where the platen is actively disengaged from the mold, typical of two-shot molding applications.
Ejector pins ensure the molding process's success in various applications. They're an important part of the molds' ejection system, which plays a vital role in product manufacturing through the injection molding process.
The metal injection mold comprises two parts: Single sides and double-sided mode of operation. Then, after the metal melts within the mold and is cooled, the platform with stacked pieces is dismantled to remove the solid plastic. Injection molds that lift the A-side half while leaving the repaired part and the B-side open are crafted. Ejection pins are positioned on the B-half of the mold cavity and function to push the formed part to be ejected out of the mold (pinning action). Usually branded on finished products with an indent, the pin badge is one of the oldest forms of security marking.
The plastic downstream product of an injection molding machine is divided into two parts, separated by the sides of two molds. This parting line area is called a divider (mold has a line). The division of the type of injection into two parts is known as a split mold, where the two skids shape the mold cavity. The mouth is fed by the diagonal score line on the nozzle side and is opened by the sides to graze the diagonal when the pull tab opens the mold. These plastic pieces are removed from the machine.
The jaw can also be directed on either the ejector or depression side. Then, after opening the mold, they go through the mowing process, which is very often hydraulic cylinders, but it can also be mechanical, using springs or air.
One of the clamping unit's main tasks is to open and close the injection mold and eject the workpieces injection-molded by the ready clamping unit. Generally, the two main clamping systems are hydraulic and toggle brackets. The hydraulic clamp system utilizes cylinders (one or a few), whereas the toggle clamp system uses a linkage column (the series).
In the clutch unit, the two large press-down plates press the injection mold. A mold is a system that includes two steel parts plates inserted into large plates of the clamping unit. This is seen when the machine is electrically connected to the electrode to melt and inject the liquid plastic into the cavity or mold when the clamping unit has fully closed the two separate plates. It allows the plastics to materialize the cavity and create the object. The melting is carried out first, and then the plastic component is further processed to become solid. The exterior of the plastic is hot enough, so if it becomes close to the injection mold, the clamping unit will now open, and part will fall out of the mold halves and be put in the collection bin.
Injection molding machines comprise various components, predominately the injection unit, which consists of other elements. The function of the injection and passive unit is to melt the input and channel it into the mold cavity. The mixing part includes the hopper, the barrel, and the rotating screw. The polymer beads will be first dried and pumped into the hopper, where the coloring pigment or other reinforcement additives will be passed through.
Next, the granules are directed inside the barrel, where they go through the heating, mixing, and moving-toward-the-mold processes, all due to the rotating screw mechanism.
The hydraulic system or unit is a critical plastic injection-molding machine family component. The process may be conducted around the clock per the production performance timelines. The nozzle manner, embedding the plunge screw, a rotation of the extruder screw, and an intense mold clamping point are, to a large extent, motion-activated and, therefore, components of dedicated sub-circuits. The plastic particles of a coarse size must pass through the mold smoothly when it comes to a heated state and then should be fed under the action of the small shift to the mold due to screw rotation and plunging phase. Any distorted motion might affect the final quality of the injection mold, which was made utilizing hydraulic motions.
DKM is a leading plastic injection maker in China that provides plastic injection molding machine services. The prime objective of this brand is to reach out to the global market trade that seeks a highly accurate plastic injection machines for their production needs. DKM manufactures various types of injection molding machines for industries and aspires to be a good service provider for industries that need molding machines. It offers the best solution to tackle your problem as its steadfastness and speedy delivery meet most of your demands. Being a kind of injection molding equipment manufacturer and injection molding machine supplier, DKM is one of the leading industries here.
